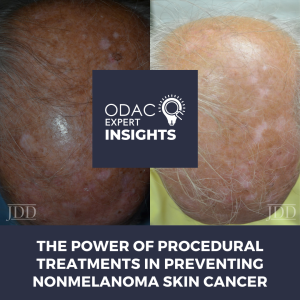
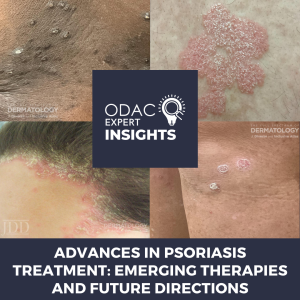
Dr. Kala Hurst recently attended ODAC dermatology conference and published her experience on Next Steps in Derm.
A First-Time Attendee’s Experience at ODAC 2025: A Conference Worth Attending
As a first-time attendee at the 2025 ODAC Dermatology Conference, I was beyond impressed with my experience. From the expertly curated sessions to the invaluable networking opportunities, ODAC delivered an immersive and engaging educational experience. If you are considering attending in the future, let me assure you it is absolutely worth it.
A Dynamic Learning Experience
ODAC Dermatology Conference’s structure kept attendees engaged with a series of one- to two-hour sessions, each consisting of digestible 15- to 20-minute presentations. These talks, led by renowned experts in dermatology, covered a diverse array of cutting-edge topics, including new treatments for alopecia, breakthroughs in systemic medications, and advances in the management of neutrophilic dermatoses. The high-yield nature of these sessions ensured that attendees walked away with practical pearls they could immediately apply in their practice. My notebook was filled with valuable insights and takeaways from the sheer volume of groundbreaking information presented.
Hands-On Learning: Live Demonstrations and Workshops
Beyond lectures, ODAC offered a hands-on approach to learning through live demonstrations and workshops. Watching expert injectors perform filler and botulinum toxin injections provided attendees with real-time insight into advanced aesthetic techniques. The workshops on deroofing for hidradenitis suppurativa, suturing techniques, and wound dressings all led by specialists in the field, were particularly enlightening, offering step-by-step guidance. These interactive sessions allowed attendees to gain confidence in procedures that they may not have been exposed to in residency or everyday practice.
Unparalleled Networking Opportunities
ODAC Dermatology ConferenceOne of the standout aspects of ODAC was its emphasis on networking. The conference’s exhibit hall featured an impressive array of pharmaceutical, OTC, and device companies showcasing the latest in dermatologic treatments and technologies. But what truly set ODAC apart was the intimate networking events, such as coffee talks with faculty and session leaders. These informal gatherings provided the rare opportunity to engage with thought leaders in dermatology, ask candid questions, and learn more about their professional journeys. As a dermatology resident, I found these discussions particularly inspiring and valuable in shaping my career path.
Resident-Focused Programming
This dermatology conference demonstrated a strong commitment to resident education through dedicated sessions tailored to the unique needs of those in training. The Derm In-Review Board Review sessions covered all major dermatology topics, offering an excellent opportunity for residents to reinforce their knowledge. Additionally, a newly introduced session on engaging with industry and expanding professional networks was met with great enthusiasm. Many residents took full advantage of this opportunity to connect with industry leaders, ask about non-traditional career paths, and explore potential collaborations beyond clinical practice.
Why You Should Attend ODAC
If you’ve been contemplating whether ODAC is worth attending, I can confidently say that it is. Not only is the conference set in the beautiful backdrop of Orlando, but it also provides an unrivaled educational experience that blends practical clinical insights, hands-on learning, and professional development. Whether you are a practicing dermatologist looking to stay ahead of the curve or a resident eager to enhance your knowledge and connections, ODAC is a must-attend event.
Mark your calendars for January 16-19, 2026—I’ll see you there! Register now.
Next Steps in Derm is the source of this article and was republished with permission. View the original article and more at nextstepsinderm.com