This webinar was previously recorded on July 1, 2020 and is now available on demand.
In Partnership with The Journal of Drugs in Dermatology
This webinar was previously recorded on July 1, 2020 and is now available on demand.
ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic & Surgical Conference’s Medical Director, Dr. Adam Friedman, discusses the ODAC 2021 program, reasons to attend and more!
To view the full agenda, click here: https://orlandoderm.org/agenda/
ODAC Dermatology Conference, in partnership with Next Steps in Derm, interviewed Dr. David Miller, Instructor in Dermatology and Medicine at Harvard Medical School and member of the Department of Dermatology and the Department of Medicine at Massachusetts General Hospital, where he is co-director of the Merkel cell carcinoma treatment program. Watch as he shares important updates on Immuno-Oncology (IO) strategies for melanoma.
Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference, interviewed Dr. Vic Ross, Director of the Scripps Clinic Laser and Cosmetic Dermatology Center in San Diego, CA, on his approach and the various interventions he uses for the treatment of Melasma. Watch as he shares fresh practical pearls immediately useful in your practice.
According to ODAC Vice-Chair Dr. Joel Cohen, Director of AboutSkin Dermatology (Greenwood Village and Lone Tree, Colorado), and Associate Clinical Professor at the University of California at Irvine, the pendulum is swinging back to heavy resurfacing in areas such as around the mouth and around the eyes that really need it. He uses full-field erbium resurfacing and shares why this is the way to go.
Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference interviewed Drs. Susan Weinkle and Jackie Yee to get their expert opinion on how to train the aesthetic eye. Watch as they share their views from a dermatologist and a plastic surgeon perspective.
So many diseases, so few FDA approved indications. Between the mind-numbing time and cost from bench to bottle, it is no surprise that dermatologists, as masters of the integument are the off-label bandits, marrying their wealth of knowledge on the pathophysiology of skin diseases to the mechanisms by which medications work to create an evidenced-based armament of therapies for both common and rare diseases alike. Where a primary care physician sees a blood pressure medication, a dermatologist sees an effective medication for acne. A medication for malaria you say? They use it for a plethora of complex diseases ranging from Lupus to scarring hair loss. The lengthy list of medications used off-label in dermatology continues to grow and for good reason and fortune.
Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference interviewed Dr. Adam Friedman, Professor, Interim Chair of Dermatology, and Residency Program Director at George Washington University, who shared off-label uses of drugs such as Hydroxychloroquine (currently under investigation for the treatment of patients with COVID-19), Pentoxifylline, and Colchicine. A wealth of clinical pearls you don’t want to miss!
Additional video pearls can be found here.
Clinical photography is a critical tool for the dermatologist and has rapidly become standard of care in the digital era. While a point-and-click approach to photography is sufficient for some circumstances, there are some simple tricks and techniques that will elevate your photography to a new level of professionalism.
Next Steps in Derm, in partnership with ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference interviewed Dr. Justin Finch, Associate Professor of Dermatology at UConn and Co-Founder of Central Connecticut Dermatology who shared his top 3 pearls for improving clinical photography in your practice.
During the 2020 ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic and Surgical Conference, Dr. Amy McMichael, Professor and Chair of Dermatology at the Wake Forest University School of Medicine, sat down with Next Steps in Derm to share important updates regarding treatments on the horizon for the most common forms of hair loss. Dr. McMichael will be presenting at Skin of Color Update 2020 with lectures including Hair & Scalp Disorders in SOC: Diagnostic Approaches and Hot Topics & Controversies in Photoprotection: Making sense of it all.
Source: Next Steps in Dermatology
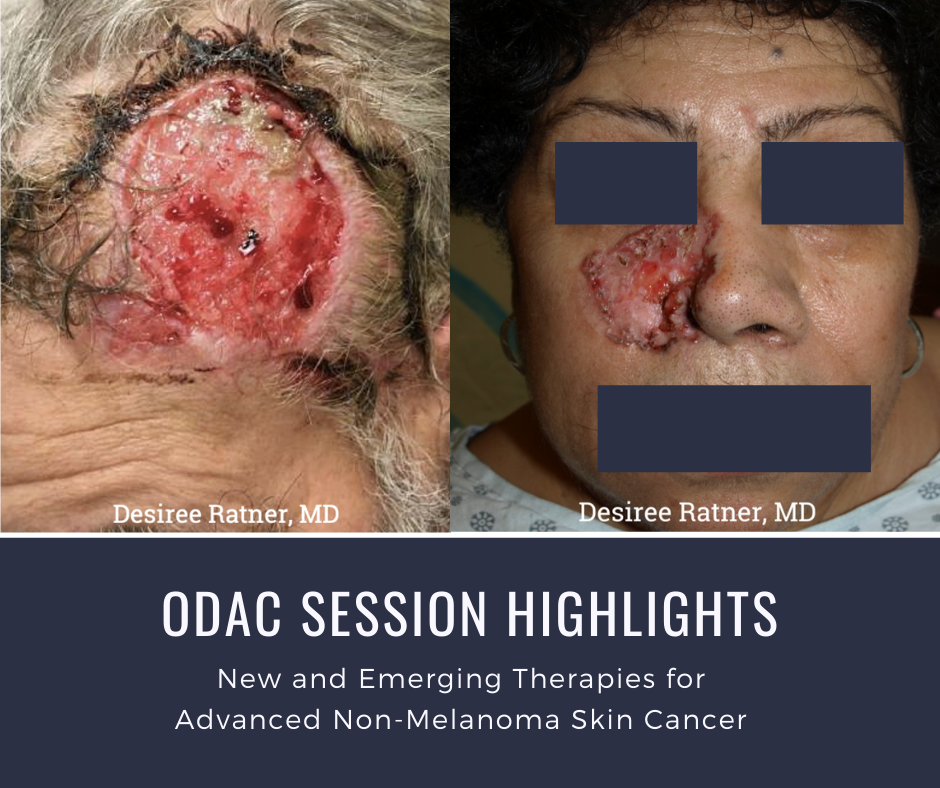
At the 17th Annual ODAC Dermatology, Aesthetic, and Surgical Conference (ODAC) held January 17-20 in Orlando, FL, Dr. Desiree Ratner led a discussion on new and emerging therapies for advanced non-melanoma skin cancer discussion.
Treatment Options
The session covered several treatments for patients including patidegib gel 2% and 4% applied once or twice daily in patients with basal cell carcinoma. Patidegib is a topical hedgehog inhibitor made by PellePharm and its mechanism of action is to block Smo signaling, thereby inhibiting the hedgehog pathway that contributes to the development of basal cell carcinomas. This treatment has several advantages in that it does not contribute to hair loss, taste loss, or muscle cramps. It has the potential to treat and mitigate facial basal cell carcinomas in basal cell nevus patients. It is being studied in randomized clinical trials enrolling patients with Gorlin’s syndrome (basal cell nevus syndrome) in the United States and in Europe.
Hedgehog pathway inhibitor resistance is unusual but may occur as “rebound” tumor growth after drug cessation or secondarily after long-term smoothened inhibitor therapy. Resistance to hedgehog pathway inhibitors is classified into primary and secondary resistance. Primary resistance has been postulated to bypass mechanisms of genes downstream of smoothened, such as the G497 W mutation. Secondary resistance in patients who showed an initial response has actually been thought to be due to de novo mutations located on regions in smoothened to which hedgehog pathway inhibitors bind or selective clonal expansion of minority clones in the pre-treated tumor. Further studies are definitely needed to elucidate what drives resistance to hedgehog pathway inhibitors and how basal cell carcinoma resistance may be overcome by other novel, emerging therapies.
Patient Cases
Dr. Ratner presented a number of interesting patient cases with advanced basal cell carcinomas sometimes so large that patients lose mobility and function of a body part or organ. In most cases, locally advanced BCCs respond well to oral hedgehog inhibitors, which can be used for long-term control or neoadjuvantly prior to surgery. In the case of one patient, an aggressive orbital BCC caused contraction of the tissues around his eye, such that he was not able to open it. Despite treatment with an oral hedgehog inhibitor, his tumor continued to grow, resulting in destruction of his orbit and locoregional metastasis.
Samples of his tumor and normal skin were sent to Stanford University, which performed whole exome sequencing. In the studies of these samples, it became evident that the tumor should have responded to vismodegib but had developed resistance due to another as yet unknown mechanism. Therapies designed to override resistance such as second-generation smoothened inhibitors are under development.
